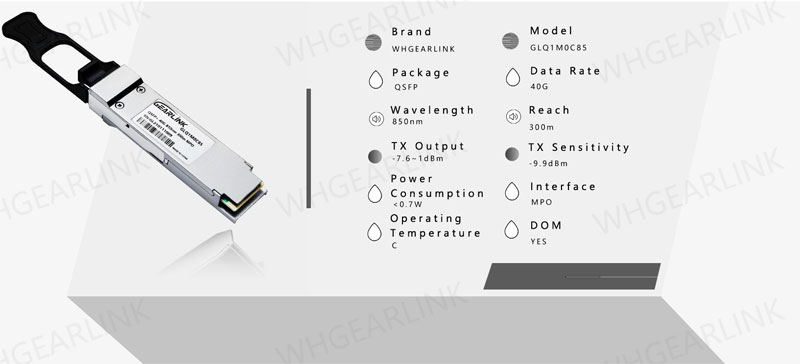
The operating temperature of the optical transceiver is divided into three types: commercial-grade(C), extended-grade(E) and industrial-grade temperature(I), specific optical modules can only be used in specific temperature environments. Commercial temperature and industrial temperature are common used. They have the following differences:
①Working temperature:
Commercial: 0~+70℃
Extended: -20~+85℃
Industrial: -40~+85℃
②Working environment:
Commercial-grade optical transceivers are generally used in comfortable network environments such as corporate networks, data centers, and computer rooms.
Industrial-grade ones are used in relatively harsh environments with large operating temperature differences, such as remote mountainous areas, tunnels, etc.
③Test method:
C-grade is subjected to room temperature aging, and the temperature is 0~+70℃. But I-grade optical module needs to be tested for high and low temperature aging, and the temperature can withstand up to 85 degrees. In an environment below 0℃, the modules are Can work stably.
④Importing of temperature compensation software:
I-grade should import temperature compensation software, which is used to ensure that the optical module has a stable supply of working current. When the temperature changes, the temperature compensation software will take effect. C-grade do not require temperature compensation, so the cost of material and manufacturing will not increase.
When purchasing an optical module transceiver, in addition to the working temperature, the working environment, data rate, transmission distance and transceiver compatibility matrix should also be considered to avoid mistakes. Besides, try to find a professional optical module manufacturer with good reputation.