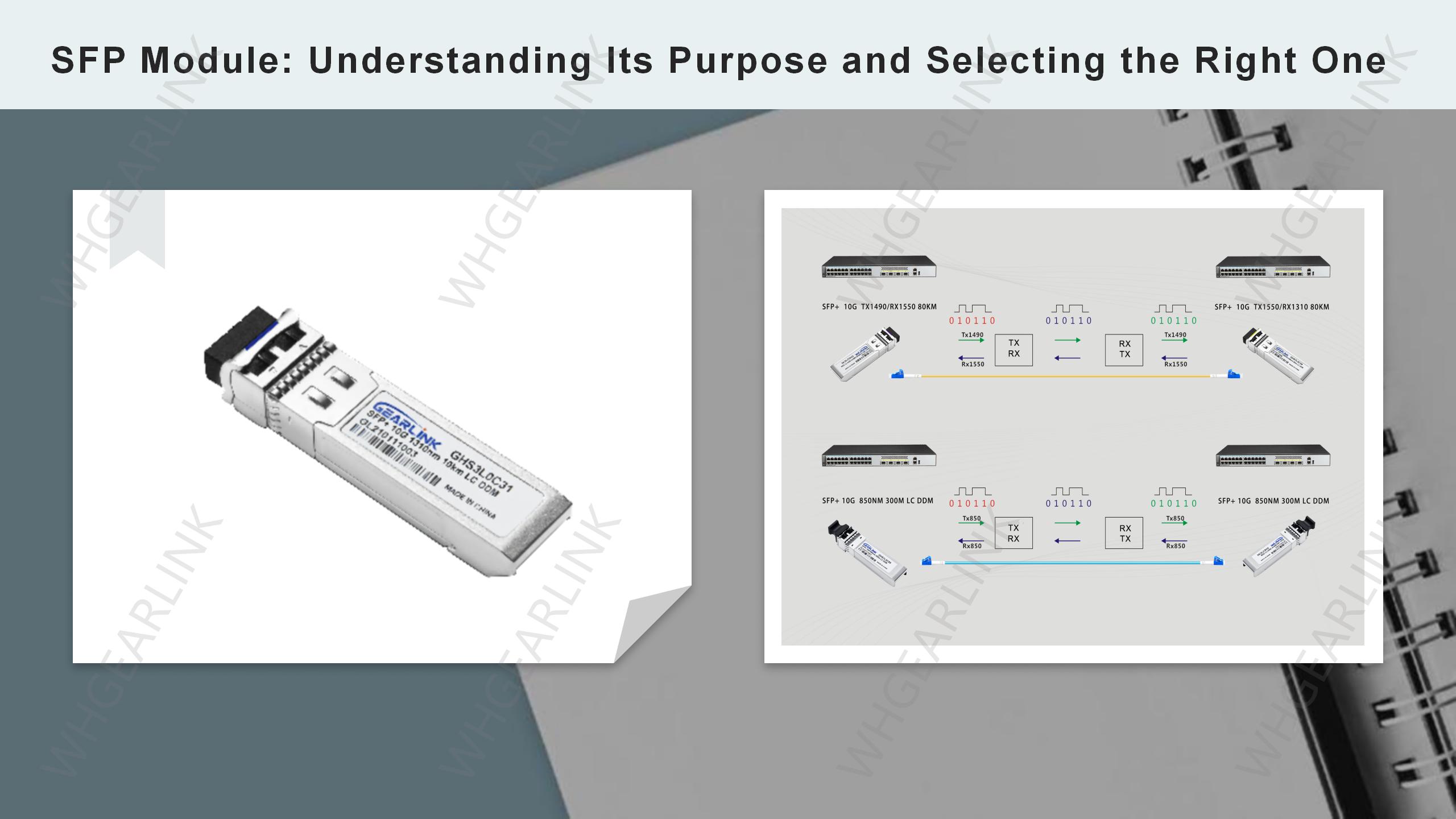
The SFP optical transceiver is currently the most used optical transceiver in the global market and has been a reliable and important component in a variety of networks for many years, including SONET, Gigabit Ethernet, Fibre Channel, PON and other applications. This guide aims to provide beginners with useful tips and information about the SFP transceiver.
An SFP transceiver, also known as a Small Form-factor Pluggable transceiver, is a hot-swappable transceiver used in networking and communication devices. It is a compact optoelectronic converter transceiver that transmits and receives data over fiber optic cables or cables.SFP optical transceivers are commonly used in switches, routers, and other network devices that are capable of carrying high-speed data transmissions. The SFP transceiver is designed to be easily inserted and removed from its corresponding slot, allowing for quick and convenient installation or replacement without disrupting the entire network. It supports various communication protocols and data rates, making it versatile and adaptable to different network requirements.
SFP transceivers can transmit over different distances depending on the wavelength. Different types of sfp transceivers can be used with both single-mode and multimode fibers, as well as copper cables, depending on the specific transceiver and its compatibility. These transceivers provide flexibility in network design and allow for easy upgrades or modifications as network needs evolve. They enable the use of different types of optical fibers or copper cables, allowing for the transmission of data over short or long distances.
Overall, the SFP optical transceiver as an important part of the modern network, for the network operation and maintenance personnel to provide more flexible operation, to achieve rapid upgrading iteration. SFP optical transceiver to continue to play an important role in the field of network, for the network to provide an important guarantee of stable connection.
Choosing the right Ethernet SFP transceiver requires considering several factors to ensure SFP transceiver compatibility and optimal performance. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind:
Data Rate: Determine the data rate required for your network. Currently, there are two types of SFP transceivers available on the market, such as 1Gbps and 155M. Please choose the transceiver that matches the data rate supported by your network equipment.
Fiber Type: Consider the type of fiber optic cable used in your network. SFP transceivers support both single-mode and multimode fibers. Single-mode fibers are suitable for long-distance transmissions, while multimode fibers are typically used for shorter distances within a building or campus. Ensure that the SFP transceiver is compatible with the fiber type you are using.
Transmission Distance: Evaluate the distance over which you need to transmit data.SFP transceivers are available in different transmission ranges such as short range (SR) up to 550, medium and long range (LR) up to 20km, extended range (ER) up to 40km and longest range (ZR) up to 100km. Choose a transceiver that can cover the required distance without signal degradation.
Connector Type: Consider the connector type used in your network infrastructure. SFP transceivers are available with different connector options, such as LC, SC, or RJ 45. Ensure that the transceiver’s connector matches the connectors on your network equipment and fiber optic cables.
Compatibility: Verify the compatibility of the SFP transceiver with your network equipment. Check the specifications and compatibility lists provided by the manufacturer to ensure that the transceiver is supported by your switches, routers, or other networking devices.
Quality and Reliability: Choose SFP transceivers from reputable manufacturers to ensure quality and reliability. Look for transceivers that comply with industry standards and have a good track record of performance and durability.
By considering these factors, you can choose an Ethernet SFP transceiver that is compatible with your network infrastructure, meets your performance requirements, and provides a reliable and cost-effective solution.
Can I use any Ethernet SFP transceiver with my existing network equipment?
Compatibility is crucial. Ensure that the transceiver you choose is compatible with your specific networking devices.
Are single-mode or multi-mode Ethernet SFP transceivers better?
It depends on the distance requirements of your network. Single-mode is suitable for long distances, while multi-mode is ideal for shorter distances.
What is hot-swappability, and why is it important?
Hot-swappability allows you to replace or upgrade transceivers without shutting down the network, ensuring minimal downtime.
Do Ethernet SFP transceivers support different data transfer rates?
Currently, optical transceivers in the form of SFP packages only support Gigabit and 100 Gigabit rates.
How do I ensure the longevity of my Ethernet SFP transceiver?
Follow recommended maintenance procedures and environmental guidelines provided by the manufacturer to ensure the longevity of your transceiver.

