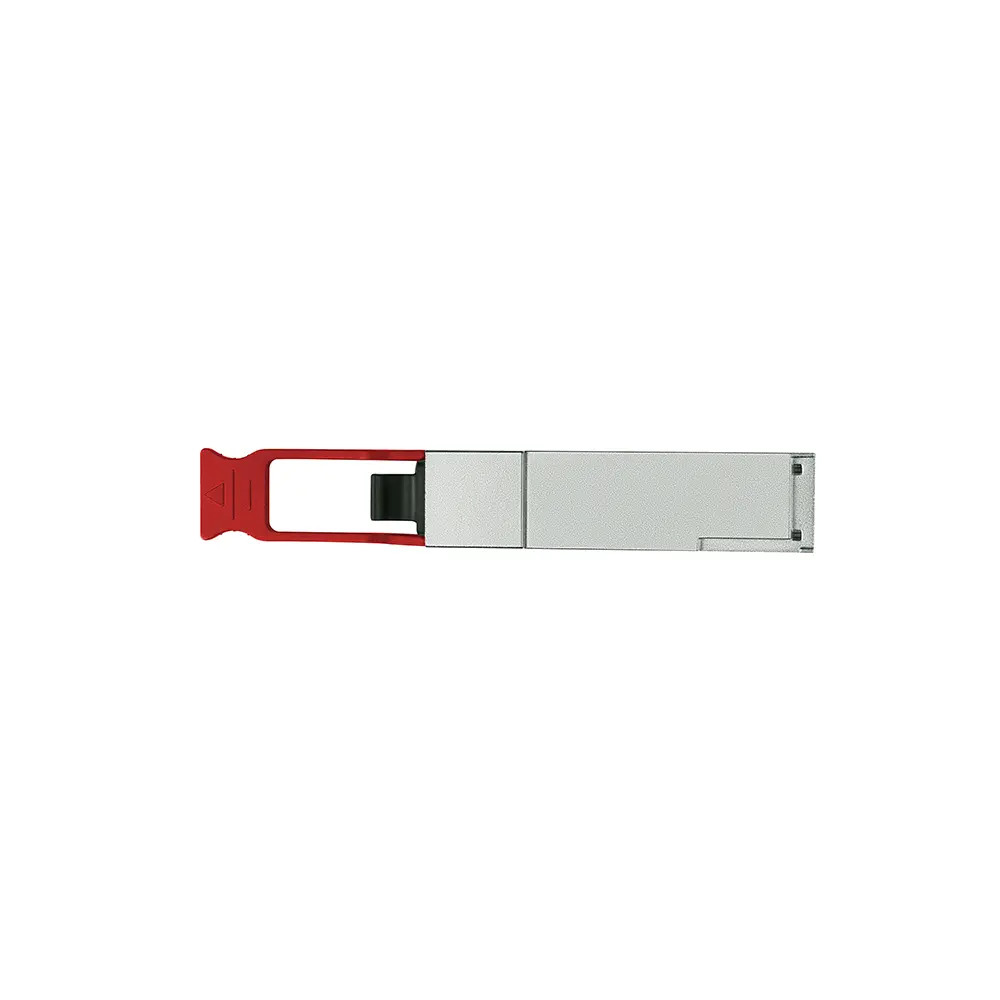
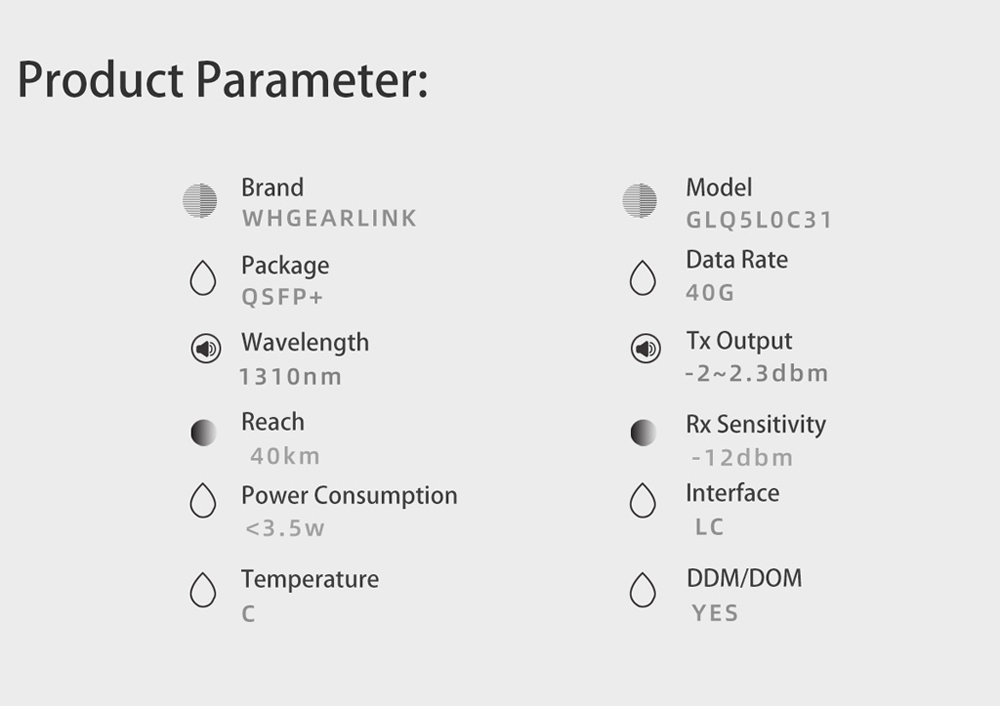
GLQ5L0C31 40g DWDM is designed to operate over single-mode fiber system using 4X10 CWDM channel in 1310 band and links up to 30km. The module converts 4 inputs channel of 10Gb/s electrical data to 4 CWDM optical signals, and multiplexes them into a single channel for 40Gb/s optical transmission. Reversely, on the receiver side, the module optically de-multiplexes a 40Gb/s input into 4 CWDM channels signals, and converts them to 4 channel output electrical data.
The central wavelengths of the 4 CWDM channels are 1271, 1291, 1311 and 1331 nm. The 40g dwdm transceiver contains a duplex LC connector for the optical interface and a 38-pin connector for the electrical interface. Single-mode fiber (SMF) is applied in this module. This product converts the 4-channel 10Gb/s electrical input data into CWDM optical signals (light), by a 4-wavelength Distributed Feedback Laser (DFB) array. The 4 wavelengths are multiplexed into a single 40Gb/s data, propagating out of the transmitter module via the SMF. The receiver module accepts the 40Gb/s optical signals input, and de-multiplexes it into 4 CWDM 10Gb/s channels. Each wavelength light is collected by a discrete photo diode, and then outputted as electric data after amplified by a TIA.
The 40g DWDM is designed with form factor, optical/electrical connection and digital diagnostic interface according to the QSFP+ Multi-Source Agreement (MSA) and compliant to 40G QSFP+ LR4 of IEEE 802.3ba.
| QSFP-40G-ER4 | 40GBASE-ER4 QSFP+ SMF 1271~1331nm 40km |
| SRX-40G-QSFP-ER4 | 40GBASE-ER4 QSFP+ 40km |
| JL306A | 40GBASE-ER4 QSFP+ 1310nm 40km |
| E40GQSFPER | 40GBASE-ER4 QSFP+ 1271~1331nm 40km |
Parameter | Symbol | Min. | Typ. | Max. | Unit | Note |
Storage Temperature | Ts | -40 | - | 85 | ºC | |
Relative Humidity | RH | 5 | - | 95 | % | |
Power Supply Voltage | VCC | -0.3 | - | 4 | V | |
Signal Input Voltage | Vcc-0.3 | - | Vcc+0.3 | V |
Parameter | Symbol | Min. | Typ. | Max. | Unit | Note |
Case Operating Temperature | Case | 0 | - | 70 | ºC | Without airflow |
Power Supply Voltage | VCC | 3.13 | 3.3 | 3.47 | V | |
Power Supply Current | ICC | - | 1060 | mA | ||
Data Rate | BR | 10.3125 | Gbps | Each channel | ||
Transmission Distance | TD | - | 30 | km | ||
Coupled fiber | Single-mode fiber | 9/125um SMF | ||||
The difference between CWDM optical transceiver and ordinary optical transceiver :
① Save more fiber resources
Compared with ordinary optical transceiver s, CWDM optical transceiver s use fewer fibers. The CWDM optical transceiver multiplexes multiple signals of different wavelengths into one signal through a multiplexer, and then transmits it to the receiving end through a single optical fiber. The receiving end demultiplexes one signal into multiple different wavelengths through a demultiplexer. The signal is transmitted to the corresponding device. Ordinary optical transceiver s need to use one optical fiber to transmit one wavelength, and multiple optical fibers must be used to transmit multiple waves, so CWDM optical transceiver s save more fiber resources than ordinary optical transceiver s.
②Working wavelength is different
CWDM optical transceiver s have a total of 18 working wavelengths (1270-1610nm), each working wavelength interval is 20nm, and there is only one working wavelength for ordinary optical transceiver s, commonly used are 850nm, 1310nm, 1490, 1550nm.