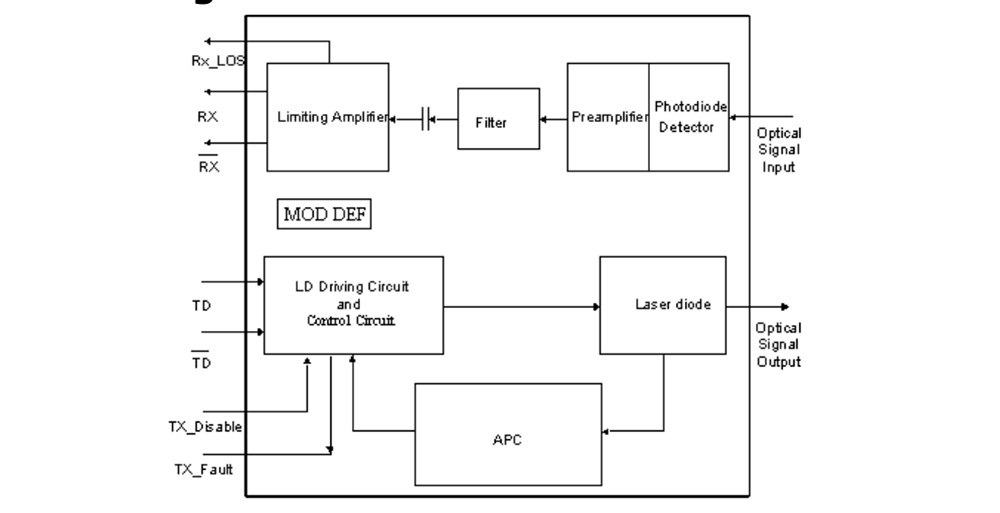
The optical module transceiver is composed of optoelectronic devices, functional circuits board and optical interfaces. The optoelectronic device includes two parts which can perform the function of transmitting and receiving.
The function of the optical transceiver module is to convert the electrical signal into an optical signal at the transmitting end. After transmitting through the optical fiber, the receiving end converts the optical signal into an electrical signal.
Although the package, speed, and transmission distance of the fiber optic transceiver are different all the internal composition and functions are basically the same.