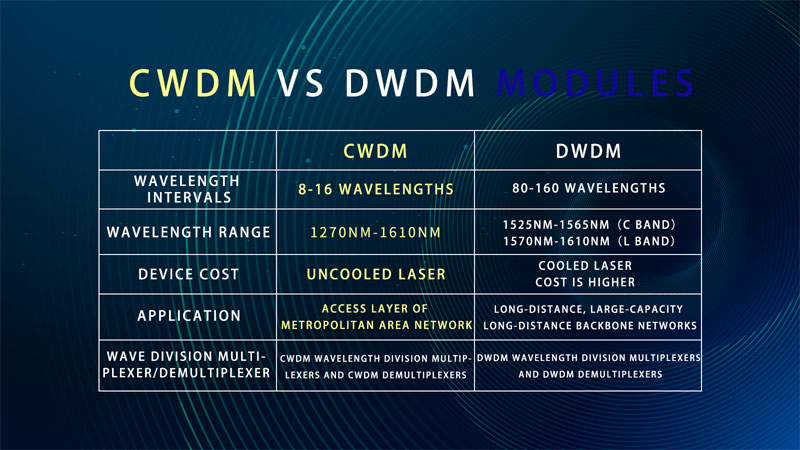
① Wavelength intervals
CWDM carrier channel spacing is wider, and each band is separated by 20nm. Therefore, only 8 to 16 wavelengths can be multiplexed on the same optical fiber. While the DWDM carrier channel spacing is relatively narrow, with 0.2nm, 0.4nm, 0.8nm, and 1.6nm intervals in each band, which can reuse 80 to 160 wavelengths.
②Wavelength ranges
The working wavelength range of CWDM is between 1270nm-1610nm, and of DWDM is selected from CWDM, which are 1525nm-1565nm (C band) 1570nm-1610nm (L band).
③Device costs
CWDM modulated laser uses uncooled laser, while DWDM uses cooled laser. The cooled laser uses temperature tuning, and uncooled laser uses electronic tuning. Due to the uneven temperature distribution in a wavelength range, temperature tuning is very difficult to achieve and the cost is high. Therefore, the cost of DWDM is much higher than CWDM.
④ Application
DWDM optical transceivers can complete the transmission of long-distance, large-capacity long-distance backbone networks. Some large-capacity metropolitan area network core nodes, telecom 5G, metropolitan area networks, backbone networks, and some data centers will also be applied to DWDM optical transceivers and devices. Compared with DWDM, the cost of CWDM will be much lower, mainly used in the access layer of the metropolitan area network, enterprise network, campus network etc. CWDM optical transceivers are widely used and save the cost of network upgrade.
⑤Wave division multiplexer/demultiplexer
CWDM optical transceivers must be used with CWDM wavelength division multiplexers and CWDM demultiplexers to achieve transmission, while DWDM optical transceivers must be used with DWDM wavelength division multiplexers and DWDM demultiplexers.